|
Evaluating a gen AI output
If you use a gen AI tool at University for assignments, always apply caution and critically evaluate the output.
Remember, gen AI is a tool, NOT a source of information. Always verify the output with credible sources.
Gen AI tools are known to make things up or 'hallucinate' if unable to find answers. Consider them as a tool to augment routine tasks, not a replacement for critical thinking, analysis and interpretation.
Here is an example of gen AI output using Microsoft Copilot.
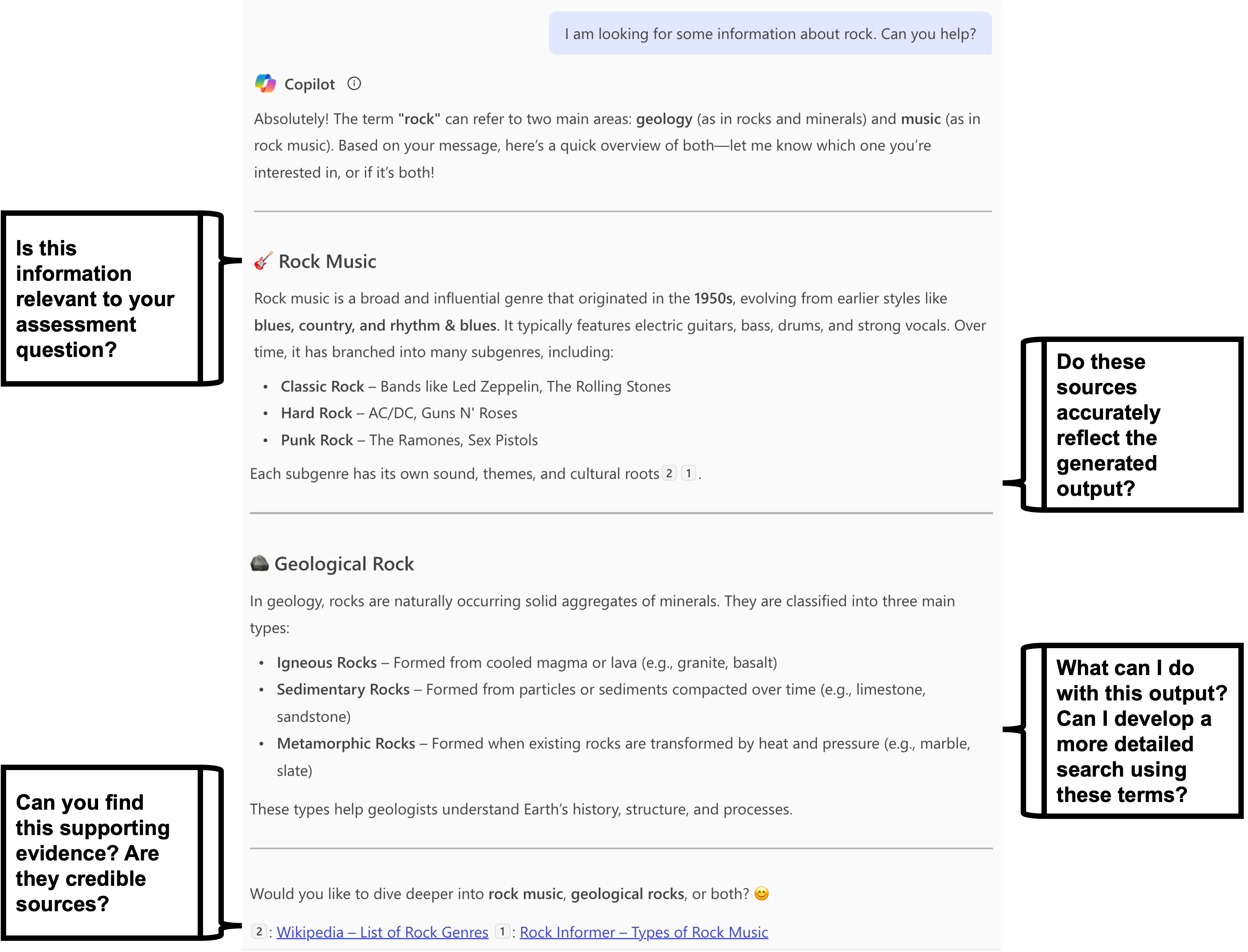
Note. Screenshot generated using Copilot (Enterprise version) [AI text generation tool], by Microsoft, 2025 (https://copilot.cloud.microsoft/).
You need to evaluate the output from any generative AI tool. Some questions to ask are:
Is the output relevant to your assignment?
- Are some sections off topic?
- Does it provide enough depth?
Can you find supporting evidence?
- Search in places such as ECU Library, Google Scholar, or the internet to find the linked sources.
Are the supporting sources credible? Take the CRAAP Test
- Use an evaluation tool (e.g. CRAAP / SIFT) to evaluate the sources linked.
Do these sources reflect the output?
- Does the gen AI output provide any links to the journal articles or sites?
- Where did the gen AI get its output from?
- Can you trace the gen AI output to a source?
What can I do with the output?
- Do not cite the output unless instructed.
- Use the key terms and concepts to build a search for databases and search engines.
- Check the referenced works and see if you can follow the information back to its original source, or to better, academic quality research.
For any output you will need to double-check whether the output and references are revelant to your purposes.
Remember, the gen AI tool does not understand what you want to use the output for, it is up to you to question the tool's output.
If you are asking follow-up questions, you may wish to analyse your own prompt to assess where it went wrong.
Even if you are following the RICE method, the gen AI tool may misinterpret your intentions or provide you with information not relevant to your topic.
Example
In the output we have some points that do not relate to our subject area:
- Music, and
- Geology
These are different definitions of "rock." We can exclude the points we don't want from our research.
Our prompt may have contributed to this issue so always try to be as definitive as possible, such as by including more detail:
rock and geology, or
Giving context like:
Act like a geology tutor, or I am a 2nd year science student
A stronger prompt may be:
Act like a geology tutor helping a 2nd year science university student develop search terms for an assessment on rock formations. Provide sources for me to verify your output.
Now the prompt returns a stronger output:
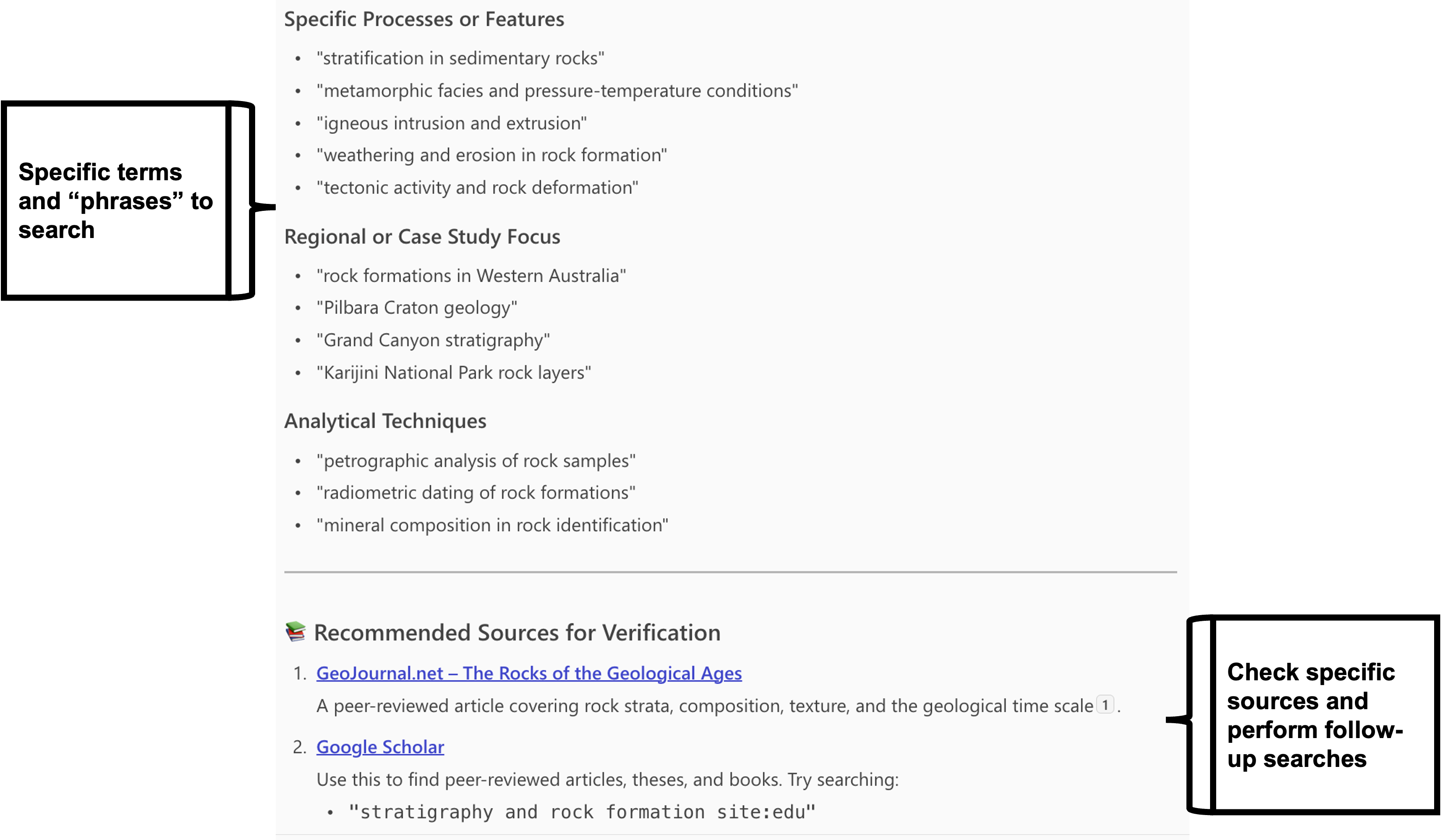
Does the output provide enough depth for your assessment?
Do not cite the output unless instructed.
The output may not go into enough detail for an academic level assessment.
This is where your own research helps you develop the gen AI tool's starting point.
Gen AI outputs will often provide links and references to the information in the output. If it doesn't you can prompt it to provide them.
Has the prompt provided you with links?
Links
If 'yes' - follow the link and identify what types of sources it has given you.
It can also be helpful to search for these sources in ECU Library Search or with tools like Ulrichsweb to help you identify whether a publication is Peer Reviewed or "Refereed."
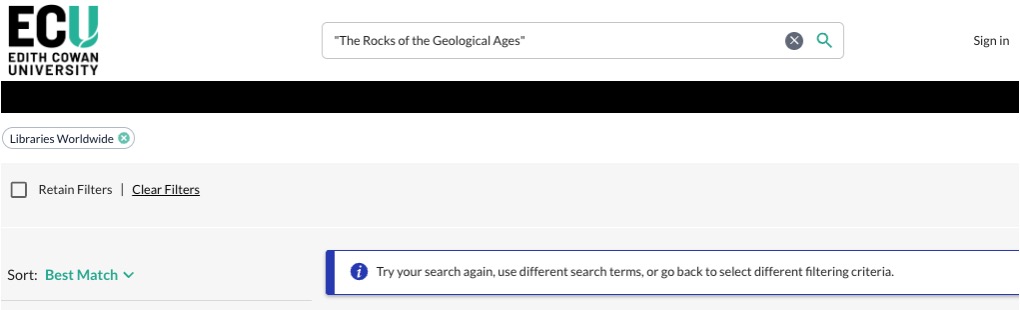
Critically, we can see that "The Rocks of the Geological Ages" does not come up in an ECU Library Search at all:
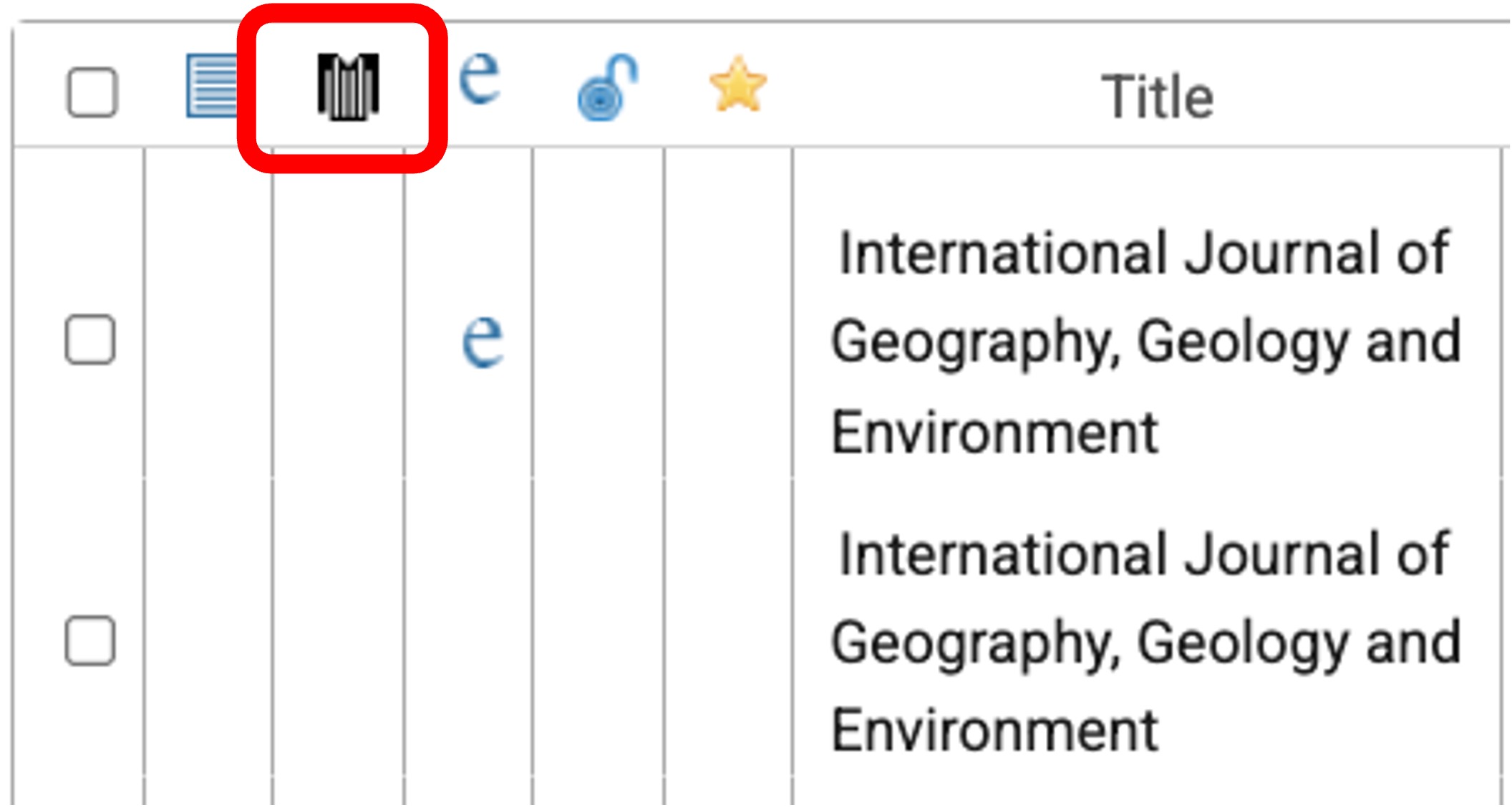
Using Ulrichsweb we find that, though the source website link claimed it was a "refereed" journal, the International Journal of Geography, Geology and Environment is not listed as refereed in the catalogue (look for the football referee's shirt icon):
No links
If it has given you a reference but no link - can you find the source by searching ECU Library Search.
Make sure to perform a "phrase search" placing the title in "quote marks" to search the exact words in that exact order.
If not - try to identify the kinds of claims the output is making, and search for appropriate evidence. For example, if it has given you statistical data, look for verification in government or industry reports. If it generates opinion regarding a topic look for multiple sources covering the issue to locate works the output has synthesised.
For help constructing search strategies, see our guide on Finding Information in Study Essentials.
For books and journal articles find the original using collections such as the ECU Library. This can provide access to paywalled articles.
Let's use our generated terms to search for articles about "Tectonic activity" AND "Rock deformation" (note I have broken the phrases down into smaller, more precise parts) using the library catalogue.
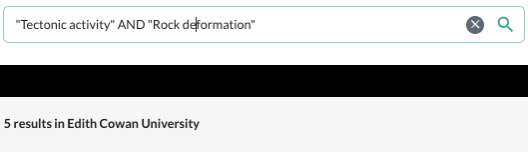
Google Scholar
If it's not available through the library try checking Google Scholar.
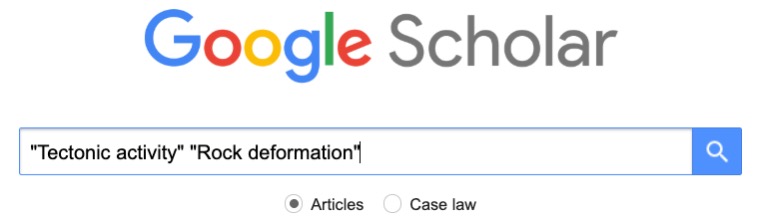
Is it a real source?
If you cannot find the source, you may need to ask yourself is it real? The source may have been fabricated by the gen AI tool due to misinterpreting your prompt, or not having enough information while still providing you with a source or reference.
Evaluate any linked articles and your own research results using the CRAAP test to identify if the sources are relevant to your assessment.
When critically evaluating any source (generative or not) consider running the material through a checklist like the CRAAP Test:
-
How Current is the work?
-
The Relevance of the material
-
What is the Authority behind the text?
-
How Accurate is it? and
-
What is the Purpose of the work?
See more in the Evaluating Sources of Information in Study Essentials.
Evaluating Sources of Information also has material on identifying Fake News, and Fact-Checking Tips.
Finally, the Search Engines and Library Databases page on Filter Bubbles & Fake News has sources you can use for fact-checking.
You must always check the credibility of your information and source, as any material you use which turns out to be inaccurate or false may lead to findings of academic misconduct.
While the use of gen AI raises the issue of inaccurate information (including intentional disinformation, deep fake images, and fake news) propagating through the news media and web, you should always try to critically assess any information you engage with.
Example
Looking at the linked article and one of the ECU Library Search results we will apply the CRAAP test.
"The rocks of the geological ages" as cited by Copilot:
Gheit, A. A. (2019). The rocks of the geological ages. International Journal of Geography, Geology and Environment, 1(1), 66-71.
- Currency: Published in 2019 it is still relatively current for geology (five year cut off for science is preferable.)
- Relevance: This article is from an academic publication but is not Peer Reviewed / Refereed. It presents general information, and little if any original research. Useful for an introductory statement but not enough as academic evidence.
- Authority: Although the article is authored by relevant experts, it has a general educationally focused viewpoint. We need additional evidence from geological science research and researchers.
- Accuracy: The article cites primarily from websites, class materials, and trade journals. This is okay for the publication but reduces credibility for our academic requirements.
- Purpose: The article and journal publication appear to be written for an educational purpose, but not at the level appropriate for a geological science student at university.
ECU Library Search (filtered to "Peer Reviewed"):
Shi, Z., Wang, G., Liu, C., & Che, Y. (2018). Tectonically induced anomalies without large earthquake occurrences. Pure & Applied Geophysics, 175(7), 2513–2526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-017-1596-9
- Currency: Published in 2018 this article may not still be current. Consider doing a citation search using Google Scholar for more recent follow-up research.
- Relevance: This is specifically a case study of tectonic anomalies, it may or may not be useful as a case study.
- Authority: It is published in an academic journal from scientists in relevant fields.
- Accuracy: It presents research evidence from academic sources.
- Purpose: This article is a Peer reviewed research paper. It may have informative research detailed through the case study, but it is an older article.
Summary: These articles either do not go into enough depth for our purposes, or are an older case study without much direct relevance to our research so other credible sources are still required. However these articles and the associated summary from Copilot can help us build an understanding of the relevant topics and provide keywords we can use in our search.
Outputs from Gen AI may not always reflect the source that has been linked.
Gen AI tools can hallucinate outputs and then misattribute their results with real sources.
Always visit the source to identify why gen AI used that source as a reference.
Misusing a source in this way could result in a finding of Academic Misconduct and is very serious.
As such, we would never rely on Copilot's output to be accurate, however, we can use the output to start further investigation.
We can use the output to help develop our search strategy and identify some information sources.
Use the key terms to find other sources.
Use the output to identify some keywords and construct a search string from them.
("Tectonic activity" OR "Continental drift") AND "Rock deformation"
See if the articles linked provide references:
Check the linked articles for references. Search for these references in the library/Google Scholar
In Shi et al. (2018), it referenced the following article. This is another older article, but may be more directly relevant, and we may wish to perform a Google Scholar citation search to find further, more current sources.
Shen, Z.-K., Lu, J., Wang, M., & Burgmann, R. (2005). Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110(B11), B11409.
Do not cite the output unless instructed
Due to the nature of LLMs the outputs do not go into enough depth for university study. Investigation and further research is required when utilising these tools and their outputs.
References
Microsoft. (2025). Copilot (Enterprise version) [AI text generation tool]. https://copilot.cloud.microsoft/
Academic Skills @ ECU
See the Academic Skills @ ECU Canvas site for more details on your responsibilities regarding Academic Integrity.
